This article explores the critical role of risk management in achieving sustainable business growth. Dive into key concepts, strategies, and case studies to understand how effective risk management can minimize losses, maximize opportunities, and enhance decision-making processes.
With this text, we continue a series of eight articles dedicated to business management.
This article presents a collection of presentation templates from the PoweredTemplate library specifically designed for risk management in business. These meticulously crafted templates visually depict essential concepts and ideas related to risk management. They serve as valuable visual aids for business professionals aiming to enhance their presentations and effectively communicate the significance of risk management to their teams and stakeholders.
Table of Contents
- Importance of Risk Management in Achieving Business Success
- Definition and Scope of Risk Management
- Understanding Risk Management
- Benefits of Risk Management for Business Success
- Implementing Risk Management Strategies
- Risk Management Techniques and Tools
- Integrating Risk Management into Business Strategy
- Continuous Improvement in Risk Management
- Conclusion
Importance of Risk Management in Achieving Business Success
Risk management plays a vital role in safeguarding the long-term viability and profitability of a business. By identifying, assessing, and effectively managing risks, organizations can mitigate potential threats while capitalizing on opportunities for growth and success. Without proper risk management practices in place, businesses are more susceptible to financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.

By implementing a robust risk management framework, businesses can proactively address uncertainties and make informed decisions. Risk management provides a structured approach to identifying and evaluating potential risks, enabling organizations to develop strategies and contingency plans to mitigate them. It also facilitates better resource allocation and helps businesses allocate their time, money, and personnel more effectively.
Furthermore, risk management enhances decision-making processes by considering potential risks and their potential impact on the business. By having a comprehensive understanding of the risks involved, businesses can make well-informed decisions that take into account both risk and reward. This helps in avoiding unnecessary risks and maximizing opportunities for growth.
In summary, risk management is a critical component of achieving business success. It allows organizations to protect their assets, minimize financial losses, optimize decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and maintain a competitive edge in the market. By prioritizing risk management, businesses can establish a strong foundation for sustainable growth and navigate uncertainties effectively.
Definition and Scope of Risk Management
Risk management can be defined as the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing potential risks to achieve specific objectives while minimizing negative outcomes. In the context of business, risk management involves analyzing the uncertainties and threats that can impact the organization’s ability to meet its goals and objectives.
The scope of risk management extends across various aspects of a business, including financial, operational, strategic, and reputational risks. It encompasses a wide range of potential hazards, such as market volatility, technological disruptions, regulatory changes, natural disasters, cybersecurity breaches, and more. Effective risk management involves understanding and addressing these risks proactively to protect the organization from adverse consequences.
The goal of risk management is not to eliminate all risks, as taking risks is an inherent part of business growth and innovation. Instead, it aims to identify, evaluate, and manage risks in a way that aligns with the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. By implementing risk management practices, businesses can strike a balance between risk-taking and risk mitigation, ensuring they are well-prepared to navigate uncertainties and seize opportunities.
It is important to note that risk management is an ongoing and iterative process. It requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adjustment to adapt to changing internal and external factors. Risk management should be integrated into the overall business strategy and decision-making processes to create a risk-aware culture within the organization.
In summary, risk management is the systematic approach of identifying, assessing, and managing potential risks in order to achieve business objectives. It encompasses a broad range of risks and requires a proactive and adaptive mindset. By embracing risk management practices, businesses can enhance their resilience, protect their interests, and increase the likelihood of long-term success.
Understanding Risk Management
Risk management involves several key concepts and principles that guide its implementation within organizations. It encompasses various activities, including risk assessment and identification, to effectively manage risks. Additionally, it is essential to have an understanding of the different types of risks that businesses may encounter.
Key Concepts and Principles of Risk Management
Risk management operates based on certain fundamental concepts and principles that provide a framework for its application. These concepts include:
- Risk Appetite
This refers to the level of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. It defines the boundaries within which risk-taking is considered acceptable and helps establish risk management strategies accordingly. - Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance is the acceptable level of variation or uncertainty an organization can withstand without compromising its objectives. It is influenced by factors such as the organization’s financial strength, industry regulations, and stakeholder expectations. - Risk Assessment
Risk assessment involves the systematic process of evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks. It helps prioritize risks based on their significance, allowing organizations to allocate resources efficiently for risk mitigation. - Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation involves implementing strategies and measures to reduce the likelihood or impact of identified risks. It may involve implementing controls, developing contingency plans, or transferring risks through insurance or contractual arrangements. - Risk Monitoring and Review
Risk management is an iterative process that requires continuous monitoring and review. Regular assessments and evaluations enable organizations to identify emerging risks, reassess existing risks, and adjust risk management strategies accordingly.
Role of Risk Assessment and Identification
Risk assessment and identification are critical components of effective risk management. By systematically identifying and analyzing risks, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of potential threats and their potential impact on the business. This enables them to make informed decisions and develop appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
Risk assessment involves:
- Identifying Risks
This entails identifying and recognizing potential risks within the organization’s internal and external environments. It involves assessing various factors, such as market conditions, operational processes, regulatory changes, and emerging trends. - Evaluating Risks
Risk evaluation involves analyzing the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks. This assessment helps prioritize risks based on their significance and assists in determining appropriate risk responses. - Quantifying Risks
Quantifying risks involves assigning numerical values or probabilities to risks and their potential impact. This quantitative assessment provides a basis for comparing risks and determining their relative importance.
Types of Risks in Business
Businesses face various types of risks that can impact their operations, profitability, and reputation. Understanding these risks is crucial for effective risk management. Some common types of risks include:
- Financial Risks
Financial risks include market volatility, credit risks, liquidity risks, interest rate fluctuations, and currency exchange rate risks. These risks can affect a company’s financial stability and cash flow. - Operational Risks
Operational risks arise from internal processes, systems, and human factors. They include supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, employee errors, cybersecurity breaches, and legal compliance issues. - Strategic Risks
Strategic risks are associated with the organization’s long-term goals and decisions. These risks include changes in market dynamics, competitive pressures, technological advancements, and disruptive innovations. - Reputational Risks
Reputational risks involve potential damage to an organization’s brand, image, or reputation. They can arise from negative publicity, customer dissatisfaction, product recalls, or ethical misconduct. - Compliance Risks
Compliance risks arise from non-compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards. Failure to adhere to legal requirements can result in legal penalties, fines, and reputational damage.
In summary, understanding risk management involves grasping key concepts and principles, recognizing the role of risk assessment and identification, and being aware of the various types of risks businesses may encounter. This knowledge provides a foundation for effective risk management implementation and helps organizations proactively mitigate potential threats.
Benefits of Risk Management for Business Success
Implementing effective risk management practices offers numerous benefits that contribute to the overall success of a business. By prioritizing risk management, organizations can minimize financial losses, maximize opportunities, enhance decision-making processes, and improve operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Minimizing Financial Losses and Maximizing Opportunities
Risk management allows businesses to identify and assess potential risks that may impact their financial stability. By understanding the potential risks and their potential consequences, organizations can implement strategies to mitigate those risks and minimize financial losses. This includes developing contingency plans, implementing internal controls, and diversifying investments.

Moreover, risk management enables businesses to capitalize on opportunities for growth and success. By identifying and assessing risks associated with potential opportunities, organizations can make informed decisions and take calculated risks that align with their objectives. This proactive approach helps businesses seize opportunities and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Enhancing Decision-making Processes
Risk management plays a critical role in enhancing decision-making processes within organizations. By considering potential risks and their potential impact, businesses can make more informed decisions. Risk assessment provides valuable insights into the likelihood and consequences of different choices, allowing organizations to evaluate potential risks and rewards.
Additionally, risk management helps businesses weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks associated with different options. This enables decision-makers to make more balanced and informed choices, taking into account the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. As a result, businesses can avoid unnecessary risks and make decisions that align with their long-term objectives.
Improving Operational Efficiency and Effectiveness
Effective risk management practices contribute to improved operational efficiency and effectiveness. By identifying and addressing potential risks in operational processes, organizations can streamline their operations, reduce disruptions, and enhance overall efficiency. This includes identifying bottlenecks, implementing risk controls, and optimizing resource allocation.
Risk management also promotes a proactive approach to risk mitigation, ensuring that potential risks are addressed before they escalate into larger issues. This minimizes the likelihood of operational disruptions, delays, and associated costs. By proactively managing risks, businesses can maintain smooth operations, deliver products or services efficiently, and meet customer expectations consistently.
In summary, implementing risk management practices offers significant benefits for business success. By minimizing financial losses, maximizing opportunities, enhancing decision-making processes, and improving operational efficiency, organizations can achieve sustainable growth and maintain a competitive edge. Prioritizing risk management allows businesses to navigate uncertainties effectively and build a resilient foundation for long-term success.
Implementing Risk Management Strategies
To effectively manage risks and ensure business success, organizations need to implement robust risk management strategies. This involves developing a risk management framework, establishing risk management policies and procedures, and allocating resources for risk mitigation.
Developing a Risk Management Framework
Developing a risk management framework provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and managing risks within an organization. This framework serves as a roadmap for implementing risk management practices consistently across the organization. It typically includes the following key components:
- Risk Management Objectives
Clearly define the objectives of the risk management process, aligning them with the organization’s overall goals and objectives. - Roles and Responsibilities
Assign roles and responsibilities for risk management activities, ensuring that accountability is established throughout the organization. - Risk Appetite and Tolerance
Define the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance levels, setting boundaries for risk-taking and guiding decision-making processes. - Risk Assessment Methods
Determine the methodologies and tools to be used for risk identification, assessment, and prioritization. This ensures a systematic and consistent approach to evaluating risks. - Risk Treatment Strategies
Establish strategies for risk treatment, including risk avoidance, risk mitigation, risk transfer, or acceptance, based on the organization’s risk appetite and assessment outcomes. - Monitoring and Reporting Mechanisms
Develop processes for ongoing monitoring, review, and reporting of risks and their management. This ensures that risks are continually assessed and appropriate actions are taken.
Establishing Risk Management Policies and Procedures
Establishing risk management policies and procedures provides a framework for implementing risk management practices consistently across the organization. These policies and procedures outline the specific steps and guidelines to be followed in identifying, assessing, and managing risks. Key considerations include:
- Risk Identification
Define the processes and methods for identifying potential risks within the organization’s various functions, departments, and projects. - Risk Assessment and Evaluation
Establish guidelines for assessing and evaluating risks, including criteria for determining their likelihood, potential impact, and significance. - Risk Treatment and Response
Outline the strategies and actions to be taken for treating and responding to identified risks, including risk mitigation, transfer, acceptance, or avoidance. - Communication and Reporting
Define the communication channels and reporting mechanisms for sharing risk-related information and updates throughout the organization. - Review and Improvement
Establish processes for regular review and improvement of risk management policies and procedures, ensuring they remain effective and aligned with the organization’s evolving needs.
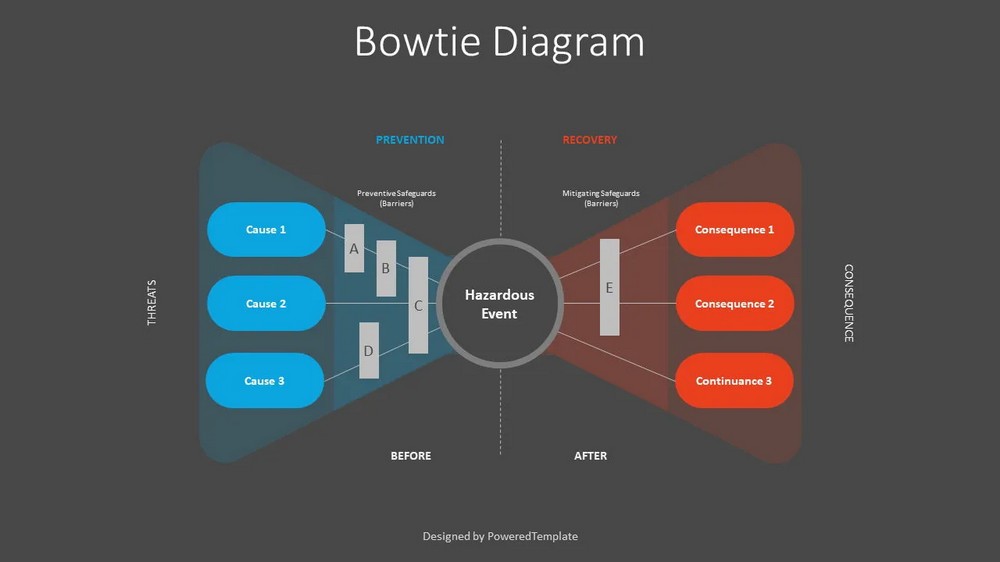
Allocating Resources for Risk Mitigation
Allocating resources for risk mitigation is essential to implement effective risk management strategies. This involves dedicating financial resources, personnel, and technological capabilities to address identified risks. Key considerations include:
- Budgeting
Allocate sufficient financial resources to support risk management activities, including risk assessment, mitigation measures, training programs, and technology investments. - Skilled Personnel
Ensure that the organization has competent personnel with the necessary skills and expertise to carry out risk management activities effectively. - Technological Support
Invest in technology solutions that facilitate risk identification, assessment, monitoring, and reporting. This may include risk management software, data analytics tools, and cybersecurity measures. - Training and Education
Provide training and educational programs to enhance risk management awareness and capabilities across the organization. This helps build a risk-aware culture and ensures that employees are equipped to identify and manage risks effectively.
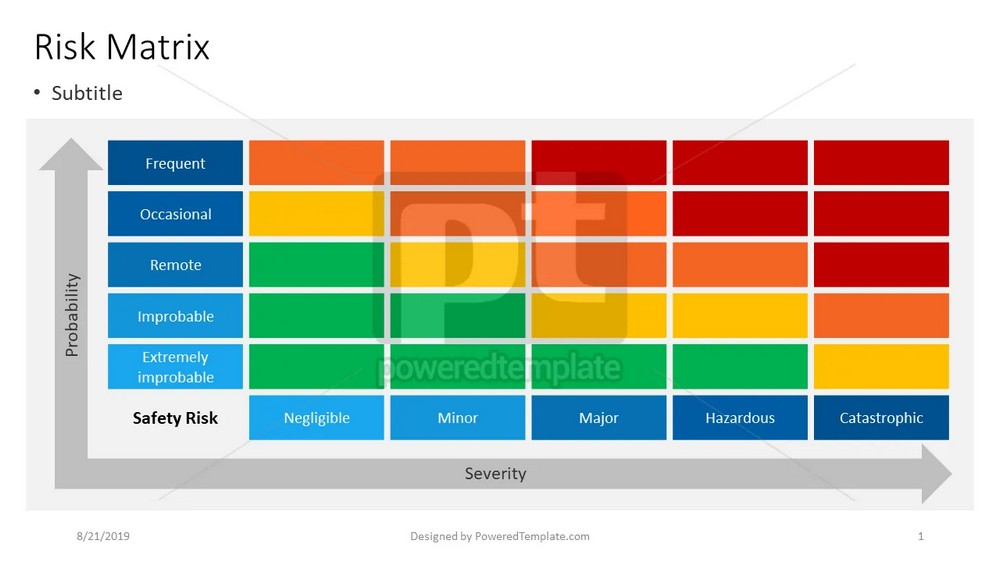
By developing a risk management framework, establishing policies and procedures, and allocating appropriate resources, organizations can implement effective risk management strategies. This enables them to proactively identify and mitigate risks, protect their interests, and maximize opportunities for sustainable business success.
Risk Management Techniques and Tools
Implementing effective risk management requires the utilization of various techniques and tools to assess, monitor, and control risks. By leveraging these methodologies, organizations can enhance their risk management practices and make informed decisions regarding risk mitigation strategies.
Risk Assessment Methodologies
Risk assessment methodologies provide a structured approach to evaluate and prioritize risks within an organization. These methodologies involve systematic processes to identify and analyze risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. Common risk assessment techniques include:
- Qualitative Risk Assessment
This approach involves a subjective assessment of risks based on expert judgment, experience, and qualitative criteria such as likelihood and impact. It provides a qualitative understanding of risks and is useful for initial risk identification and prioritization. - Quantitative Risk Assessment
Quantitative risk assessment involves assigning numerical values to risks and their potential impact. It utilizes mathematical models, statistical analysis, and data-driven techniques to quantify risks and their probabilities. This approach provides a more objective and numerical assessment of risks. - Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis involves developing hypothetical scenarios and assessing the potential impact of risks under those scenarios. It helps identify critical vulnerabilities and potential outcomes in different situations, allowing organizations to develop appropriate risk responses. - Fault Tree Analysis
Fault tree analysis is a graphical technique used to identify and analyze potential causes of risks and their associated consequences. It visually represents the relationship between events and their contributions to risk occurrence. It helps organizations understand the underlying factors leading to risks and develop targeted risk mitigation strategies.
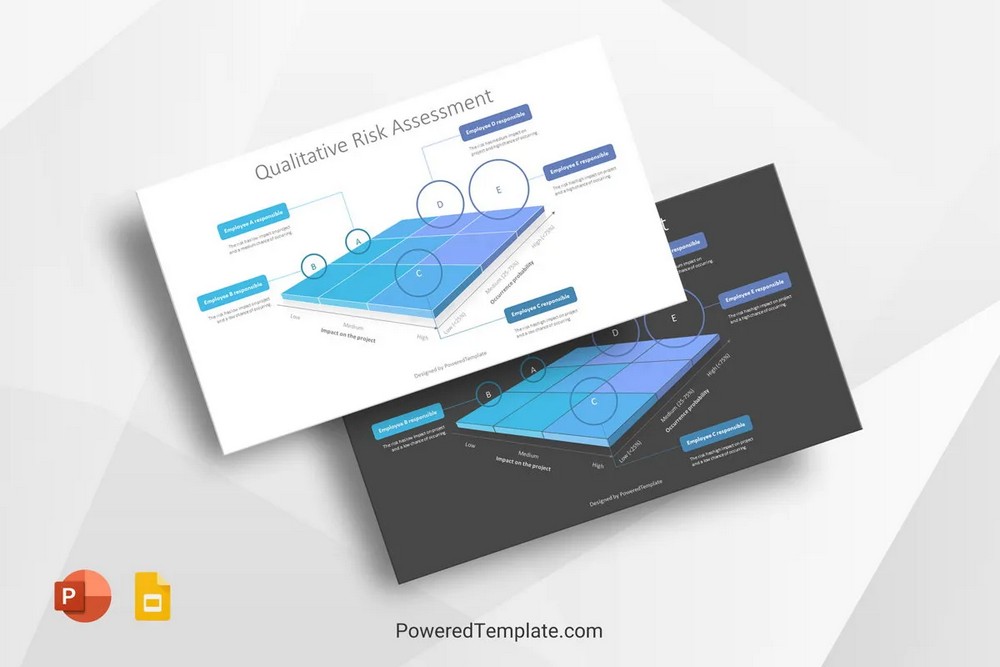
Risk Monitoring and Control Mechanisms
Risk monitoring and control mechanisms enable organizations to track and manage risks throughout their lifecycle. These mechanisms ensure that risks are continually monitored, and appropriate actions are taken to mitigate them. Common risk monitoring and control techniques include:
- Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
KRIs are specific metrics or indicators that provide early warning signs of potential risks. By tracking KRIs, organizations can proactively identify and address emerging risks before they escalate. - Risk Registers
Risk registers are comprehensive databases that document identified risks, their likelihood, potential impact, and risk response strategies. They serve as a centralized repository of risk information and facilitate ongoing risk monitoring and control. - Control Implementation
Control implementation involves establishing risk controls, such as policies, procedures, and safeguards, to minimize the likelihood or impact of identified risks. This includes implementing internal controls, segregation of duties, and compliance measures to mitigate risks effectively. - Regular Reporting and Review
Regular reporting and review processes ensure that risk information is communicated, and risk mitigation efforts are monitored. This allows organizations to assess the effectiveness of risk management strategies and make necessary adjustments as required.
Utilizing Technology for Risk Management
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing risk management practices. Organizations can leverage various technological tools and solutions to streamline risk management processes and improve efficiency. Examples of technology utilization for risk management include:
- Risk Management Software
Risk management software provides integrated platforms to capture, analyze, and monitor risks systematically. These tools enable organizations to centralize risk data, automate risk assessments, generate reports, and facilitate collaboration among stakeholders. - Data Analytics
Data analytics techniques, such as data mining, predictive modeling, and machine learning, can be employed to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and assess risks based on historical and real-time data. Data analytics helps organizations gain deeper insights into risks and make data-driven decisions. - Automated Monitoring Systems
Automated monitoring systems continuously monitor key risk indicators, detect deviations, and trigger alerts for potential risks. These systems enhance real-time risk monitoring and enable prompt risk response actions. - Cybersecurity Measures
Given the increasing cyber threats, robust cybersecurity measures are essential for risk management. Implementing firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and employee training programs can help mitigate cybersecurity risks.
By utilizing risk assessment methodologies, implementing risk monitoring and control mechanisms, and leveraging technology, organizations can strengthen their risk management practices. These techniques and tools enable a comprehensive and proactive approach to risk management, allowing businesses to effectively identify, monitor, and mitigate risks for enhanced business resilience and success.
Integrating Risk Management into Business Strategy
Integrating risk management into the overall business strategy is crucial for organizations to effectively navigate uncertainties and achieve sustainable success. This involves aligning risk management practices with organizational goals, incorporating risk management in strategic planning, and fostering a risk-aware culture within the organization.
Aligning Risk Management with Organizational Goals
Aligning risk management with organizational goals ensures that risk management activities are directly tied to the strategic objectives of the business. This alignment helps prioritize risks that have the potential to impact the achievement of organizational goals. Key considerations for aligning risk management with organizational goals include:
- Risk Appetite and Risk Tolerance
Align the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance levels with its overall goals and objectives. This ensures that risk-taking is aligned with the organization’s risk tolerance while enabling the pursuit of strategic objectives. - Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establish KPIs that include risk-related metrics to measure and monitor the effectiveness of risk management activities in relation to the organization’s goals. This enables the organization to track progress and make necessary adjustments to achieve its objectives. - Strategic Prioritization
Prioritize risks based on their potential impact on strategic objectives. This ensures that risk mitigation efforts are focused on addressing the risks that have the highest potential to hinder the organization’s strategic success.
Incorporating Risk Management in Strategic Planning
Incorporating risk management in strategic planning ensures that risks are proactively considered during the formulation and execution of the organization’s strategic initiatives. This integration helps identify potential risks and opportunities associated with strategic decisions. Key considerations for incorporating risk management in strategic planning include:
- Risk Identification and Assessment
Identify and assess risks that are associated with the organization’s strategic objectives and initiatives. This involves analyzing internal and external factors that may impact the successful implementation of the strategy. - Risk Mitigation Strategies
Develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans to address the identified risks. Consider integrating these strategies into the strategic initiatives to ensure that risk management is an integral part of the overall execution plan. - Regular Risk Reviews
Conduct regular reviews of the strategic plan to reassess and update the risk profile based on changing internal and external factors. This iterative process ensures that risks are continuously monitored, and risk mitigation strategies are adjusted as needed.
Creating a Risk-aware Culture within the Organization
Creating a risk-aware culture within the organization fosters a proactive approach to risk management across all levels and functions. It involves instilling a mindset that acknowledges the importance of identifying, assessing, and managing risks in everyday decision-making processes. Key considerations for creating a risk-aware culture include:
- Leadership Commitment
Demonstrate leadership commitment to risk management by setting the tone from the top. Leaders should prioritize risk management and lead by example in making risk-informed decisions. - Employee Engagement
Engage employees at all levels by providing training and educational programs on risk management. Encourage employees to actively participate in risk identification, assessment, and reporting processes. - Communication and Collaboration
Establish open channels of communication to encourage the sharing of risk-related information and concerns. Foster a collaborative environment where employees can collaborate on risk mitigation strategies and contribute to the overall risk management efforts. - Recognition and Incentives
Recognize and reward individuals and teams for their contributions to risk management practices. This helps reinforce a risk-aware culture and motivates employees to actively participate in risk management activities.
By integrating risk management into the business strategy, organizations can ensure that risks are considered throughout the decision-making process. This alignment enables organizations to effectively mitigate risks, seize opportunities, and achieve their strategic goals. Additionally, fostering a risk-aware culture empowers employees to proactively manage risks, enhancing the organization’s overall resilience and success.
Continuous Improvement in Risk Management
Continuous improvement is essential in risk management to adapt to changing circumstances and enhance the effectiveness of risk management practices. This section focuses on the importance of regular evaluation and review, learning from past experiences, and evolving risk management practices in response to new challenges.
Regular Evaluation and Review of Risk Management Processes
Regular evaluation and review of risk management processes are crucial for identifying areas for improvement and ensuring the effectiveness of risk management strategies. Organizations should establish a systematic approach to assess and review their risk management practices. Key considerations include:
- Performance Metrics
Define appropriate performance metrics to measure the effectiveness of risk management processes. These metrics can include the frequency and severity of risks, risk mitigation outcomes, and the timeliness of risk response. - Evaluating Risk Controls
Assess the effectiveness of implemented risk controls in mitigating identified risks. This evaluation helps determine whether the existing controls are sufficient or if adjustments or additional measures are needed. - Stakeholder Feedback
Gather feedback from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners, regarding their perception of the organization’s risk management efforts. This feedback provides valuable insights and identifies potential areas for improvement. - Compliance and Regulatory Updates
Regularly review compliance requirements and regulatory changes to ensure that risk management practices align with the latest industry standards and legal obligations.
Learning from Past Experiences and Implementing Lessons Learned
Learning from past experiences and implementing lessons learned is critical for continuous improvement in risk management. By analyzing past incidents, near-misses, and successes, organizations can identify areas of improvement and adjust their risk management practices accordingly. Key considerations include:
- Incident Analysis
Conduct thorough analyses of past incidents and near-misses to identify root causes and underlying vulnerabilities. Use these insights to strengthen risk controls, develop preventive measures, and enhance risk response strategies. - Knowledge Sharing
Encourage knowledge sharing and communication of lessons learned across the organization. Establish mechanisms such as post-incident debriefings, case studies, and knowledge repositories to disseminate information and facilitate organizational learning. - Training and Development
Provide regular training and development opportunities for employees to enhance their risk management knowledge and skills. This ensures that the organization benefits from a knowledgeable workforce capable of effectively managing risks. - Continuous Improvement Culture
Foster a culture that encourages and rewards continuous improvement in risk management. Promote innovation, creativity, and an open mindset toward finding better ways to manage risks and respond to challenges.
Evolving Risk Management Practices in Response to New Challenges
Risk management practices need to evolve in response to emerging risks and changing business landscapes. Organizations must stay vigilant and adapt their risk management strategies to address new challenges effectively. Key considerations include:
- Emerging Risk Identification
Continuously scan the internal and external environments to identify emerging risks that may impact the organization. Stay informed about industry trends, technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and other factors that may introduce new risks. - Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Review and update risk assessment methodologies and mitigation strategies to align with emerging risks. Consider integrating emerging risks into the existing risk management framework and adjusting risk mitigation measures accordingly. - Technology Adoption
Embrace technological advancements to enhance risk management capabilities. Explore tools and solutions that can automate risk monitoring, data analysis, and reporting, allowing for more efficient and effective risk management practices. - Industry Collaboration
Engage in industry collaborations and networks to share knowledge and best practices in managing emerging risks. Collaborating with peers and industry experts helps organizations stay at the forefront of risk management practices.
By embracing continuous improvement in risk management, organizations can adapt to evolving challenges, strengthen their risk mitigation strategies, and enhance their overall resilience. Regular evaluation, learning from past experiences, and evolving risk management practices ensure that risk management remains effective and aligned with the organization’s objectives in an ever-changing business landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, risk management is a powerful tool that enables organizations to navigate uncertainties, protect their interests, and achieve sustainable business success. By integrating risk management into the fabric of their operations, organizations can make informed decisions, mitigate potential risks, and capitalize on opportunities. Through continuous improvement, learning from past experiences, and adapting to emerging challenges, organizations can enhance their risk management practices and stay resilient in an ever-evolving business environment.

As businesses face increasing complexities and uncertainties, prioritizing risk management is more important than ever. By embracing the power of risk management, organizations can forge a path toward sustainable success, effectively manage risks, and create a resilient foundation for future growth and prosperity.



