This article focuses on understanding and embracing continuous improvement as a vital aspect of business management. It discusses the benefits and challenges associated with implementing such an approach, as well as strategies for successfully implementing continuous improvement in an organization.
With this text, we conclude the series of eight articles dedicated to the topic of business management.
This article highlights a selection of presentation templates from the PoweredTemplate library that are specifically designed for the topic of continuous improvement in business management. These meticulously designed templates visually depict essential concepts and ideas associated with continuous improvement. They serve as valuable visual tools for business professionals aiming to enhance their presentations and effectively communicate the significance of continuous improvement to their teams and stakeholders.
Table of Contents
- Importance and Benefits of Continuous Improvement in Business Management
- Understanding Continuous Improvement in Business Management
- Implementing Continuous Improvement in Business Management
- Tools and Techniques for Continuous Improvement
- Overcoming Challenges in Continuous Improvement
- Conclusion
Importance and Benefits of Continuous Improvement in Business Management
Continuous improvement is a fundamental approach to enhancing business efficiency and achieving long-term success, enabling organizations to establish a foundation for a culture of innovation, effectiveness, and excellence. In the following, we will explore the importance and numerous advantages that continuous improvement brings to business management.
- Enhanced Efficiency
Continuous improvement methodologies such as Lean and Six Sigma enable organizations to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, streamline processes, and optimize resource utilization. This leads to improved productivity, reduced waste, and enhanced operational efficiency. - Increased Quality
By continuously seeking ways to improve processes, products, and services, businesses can elevate the quality of their offerings. Implementing quality control measures and incorporating customer feedback helps in meeting and exceeding customer expectations, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. - Innovation and Adaptability
Continuous improvement fosters a culture of innovation within organizations. It encourages employees to think creatively, identify opportunities for improvement, and implement innovative solutions. This adaptability to change ensures that businesses stay relevant and agile in a rapidly evolving market. - Cost Savings
Through continuous improvement efforts, businesses can identify cost-saving opportunities by eliminating waste, reducing rework, and optimizing resource allocation. This can result in significant financial savings, improved profitability, and a competitive edge in the market. - Engaged Workforce
Implementing continuous improvement initiatives promotes employee engagement and empowerment. By involving employees in the improvement process and recognizing their contributions, businesses can foster a sense of ownership, motivation, and a collaborative work environment. - Competitive Advantage
Embracing continuous improvement enables businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors. By consistently improving processes, products, and customer experiences, organizations can gain a competitive edge, attract more customers, and position themselves as industry leaders.
The benefits of continuous improvement are far-reaching. It leads to enhanced efficiency, increased quality, greater customer satisfaction, and improved financial performance. By implementing effective improvement strategies and leveraging the tools and techniques available, businesses can achieve a competitive advantage and position themselves as industry leaders.
Understanding and embracing continuous improvement principles is key to achieving long-term success in business management.
Understanding Continuous Improvement in Business Management
In this section, we will delve deeper into the concept of continuous improvement, exploring its definition, key principles, and methodologies.
Definition of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement, also known as Kaizen, refers to an ongoing effort to enhance processes, products, and services incrementally. It involves a systematic approach to identifying areas for improvement, making small changes, and continuously evaluating and refining processes to achieve better results. The goal is to create a culture of continuous learning, adaptation, and growth within an organization.
Key Principles and Methodologies
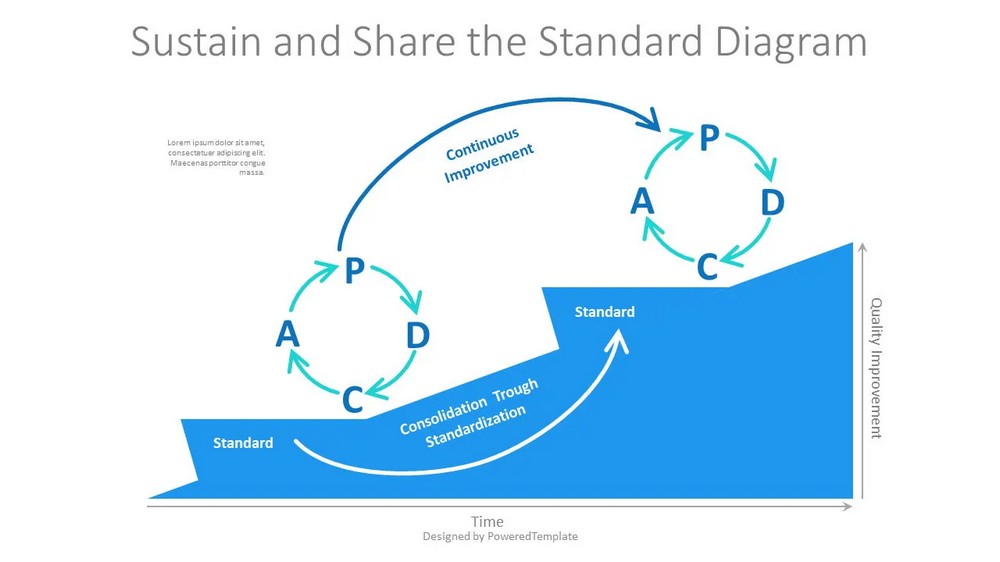
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle
The PDCA cycle, also known as the Deming cycle, is a fundamental principle of continuous improvement. It involves four stages: planning, implementing, evaluating, and taking action based on the results. This iterative process ensures continuous learning and improvement.
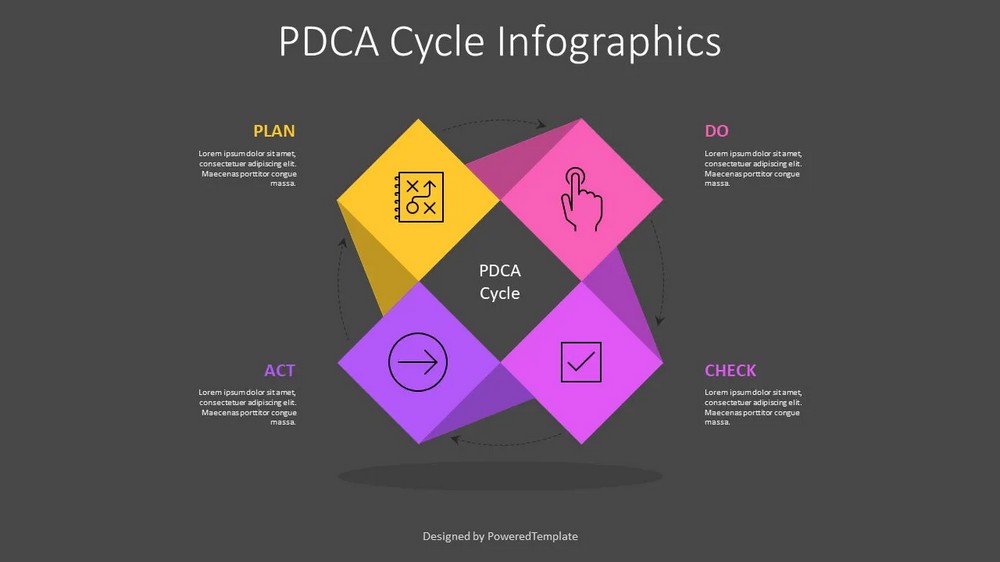
- Plan: In this initial stage, the problem or opportunity for improvement is identified, and goals and objectives are set. Data is gathered, and analysis is performed to understand the current state and determine the desired outcome. A plan is then formulated to achieve the improvement goals.
- Do: The second stage involves implementing the plan developed in the previous stage. Actions are taken to execute the planned changes or improvements. This may involve testing new processes, implementing new strategies, or making adjustments to existing systems. It is essential to document the actions taken and gather relevant data during this phase.
- Check: Once the changes have been implemented, the next stage involves evaluating the results and measuring the outcomes against the defined objectives. Data is collected and analyzed to determine the effectiveness of the implemented changes. This evaluation helps identify any gaps or deviations from the expected outcomes.
- Act: Based on the findings of the Check stage, necessary adjustments or corrective actions are taken in the Act stage. Lessons learned from the previous stages are utilized to refine the plan and make further improvements. This stage focuses on implementing sustainable solutions and incorporating the lessons learned into future processes.
The PDCA cycle is iterative, meaning that the process is repeated continuously to drive ongoing improvement. Each cycle builds upon the knowledge and experience gained from previous iterations, leading to incremental enhancements and refined processes over time.
The PDCA cycle provides a structured framework for organizations to continuously improve their operations, products, and services. It promotes a systematic approach to problem-solving and ensures that changes are based on data-driven decision making. By embracing the PDCA cycle, organizations can drive continuous improvement, enhance quality, and achieve better results.
Lean Thinking
Lean principles focus on eliminating waste, improving efficiency, and maximizing value for customers. By identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities, organizations can streamline processes and deliver products or services with minimal waste and optimal resource utilization.
Lean Thinking is a management philosophy and approach that focuses on eliminating waste, maximizing value, and continuously improving processes. It originated from the Toyota Production System (TPS) and has since been widely adopted across industries.
Key principles of Lean Thinking include:
- Value: Identifying and understanding customer needs and defining value from the customer’s perspective. Value is any activity that directly contributes to meeting customer requirements.
- Value Stream: Mapping and analyzing the end-to-end value stream, which encompasses all the activities and processes required to deliver a product or service to the customer. It helps identify non-value-added activities and opportunities for improvement.
- Flow: Optimizing the flow of value through the value stream by eliminating bottlenecks, reducing wait times, and improving the smoothness and efficiency of processes. This includes implementing strategies such as just-in-time production and pull systems.
- Pull: Adopting a pull-based system where work is initiated based on customer demand. This helps prevent overproduction, reduces inventory levels, and improves responsiveness to customer needs.
- Perfection: Striving for continuous improvement and creating a culture of learning and problem-solving. This involves setting challenging goals, engaging employees, and continuously seeking opportunities to eliminate waste and enhance processes.
Lean Thinking emphasizes the importance of engaging employees at all levels, empowering them to identify and solve problems, and promoting a culture of continuous improvement. It encourages the application of various tools and techniques such as value stream mapping, 5S (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), and Kaizen events to drive waste reduction, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.

By adopting Lean Thinking, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, improve quality, and increase customer value. It provides a systematic approach to eliminating waste and creating a lean, agile, and customer-centric organization.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at reducing defects and process variations. It involves a structured approach, utilizing statistical tools and techniques, to measure, analyze, improve, and control processes. The goal is to achieve a level of performance where the occurrence of defects is extremely low.

Key principles and concepts of Six Sigma include:
- Define: Clearly defining the problem or opportunity for improvement and aligning it with organizational goals. This involves identifying the critical-to-quality (CTQ) characteristics that are most important to the customer and setting measurable objectives.
- Measure: Collecting and analyzing relevant data to gain a deep understanding of the current state of the process and to quantify the extent of the problem. Statistical tools and techniques are used to measure process performance and identify areas of improvement.
- Analyze: Investigating the root causes of process variations and defects through data analysis. Tools such as cause-and-effect diagrams, Pareto charts, and statistical analysis help identify the key sources of variation and prioritize improvement opportunities.
- Improve: Developing and implementing solutions to address the root causes of process issues. This involves designing and testing changes, optimizing process parameters, and validating improvements through pilot projects or experiments.
- Control: Establishing control mechanisms to sustain the improvements achieved. This includes implementing monitoring systems, standardizing processes, and providing training to ensure that the improvements are maintained over time.
Six Sigma utilizes a set of statistical tools and techniques, such as hypothesis testing, control charts, and design of experiments, to guide the problem-solving and improvement process. The methodology places a strong emphasis on data-driven decision making, and projects are typically executed by cross-functional teams led by trained and certified Six Sigma professionals.

By applying Six Sigma principles and methodologies, organizations can reduce defects, improve process efficiency, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve significant bottom-line results. It provides a systematic and rigorous approach to problem-solving and process improvement, helping organizations drive continuous improvement and achieve operational excellence.
Kaizen Events
Kaizen events are intensive improvement initiatives that bring together cross-functional teams to address specific process improvement opportunities. These events focus on rapid problem-solving, encouraging collaboration, and implementing immediate changes to achieve tangible results within a short timeframe. The term “kaizen” translates to “continuous improvement” in Japanese, and these events align with the philosophy of continuous improvement in business management.
Key aspects of Kaizen events include:
- Focus: Kaizen events target a specific process, problem, or opportunity for improvement. They concentrate efforts on a particular area that requires immediate attention or has significant potential for enhancement.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Kaizen events typically involve a diverse group of stakeholders, including employees from different departments or functions. By bringing together individuals with different perspectives and expertise, the event benefits from a range of insights and fosters a collaborative approach to problem-solving.
- Time-Limited: Kaizen events are time-bound and typically last anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks. The limited timeframe encourages a sense of urgency and helps maintain focus and momentum throughout the event.
- Rapid Improvement: The primary goal of Kaizen events is to achieve rapid and tangible improvements. This is accomplished through intensive analysis, problem-solving, and the implementation of immediate changes or solutions.
- Lean Tools and Techniques: Kaizen events often utilize various Lean tools and techniques to facilitate the improvement process. These may include value stream mapping, 5S (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), Kanban, or other Lean methodologies.
During a Kaizen event, participants typically follow a structured process that involves data analysis, brainstorming, root cause identification, solution generation, and implementation planning. The event concludes with the implementation of identified improvements and a plan for sustaining the changes beyond the event.
Kaizen events can yield significant improvements in quality, productivity, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. They provide a focused and collaborative approach to problem-solving and improvement, enabling organizations to address critical issues and drive rapid change within a compressed timeframe.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive management philosophy and approach to continuous improvement that emphasizes customer focus, process improvement, and the involvement of all employees. It aims to create a quality-driven culture by implementing quality control measures, continuous training, and ongoing customer feedback loops.

Key principles and concepts of Total Quality Management include:
- Customer Focus: TQM places a strong emphasis on understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations. It involves gathering and incorporating customer feedback, identifying critical quality characteristics, and aligning processes to deliver superior value to customers.
- Continuous Improvement: TQM is centered around the idea of continuous improvement, where all individuals in the organization are engaged in identifying opportunities for improvement and driving positive change. It involves implementing problem-solving methodologies, such as Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA), and fostering a culture of ongoing learning and innovation.
- Employee Involvement: TQM recognizes that employees are key contributors to quality and organizational success. It encourages their active involvement, empowerment, and participation in decision-making processes. TQM promotes teamwork, collaboration, and provides opportunities for training and development to enhance employee skills and knowledge.
- Process Orientation: TQM emphasizes the importance of understanding and managing processes to achieve quality outcomes. It involves mapping and analyzing processes, identifying bottlenecks or areas for improvement, and implementing strategies to optimize process efficiency and effectiveness.
- Measurement and Data-Driven Decision Making: TQM utilizes measurement systems and data analysis to monitor performance, track progress, and make informed decisions. It encourages the use of statistical tools and techniques to analyze data and identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
- Supplier and Partner Relationships: TQM recognizes the importance of strong relationships with suppliers and partners. It involves collaborating closely with them to ensure the quality of inputs and promote mutually beneficial partnerships.
By implementing Total Quality Management principles, organizations can achieve a culture of excellence, enhanced customer satisfaction, and improved overall performance. TQM drives continuous improvement, employee engagement, and a customer-centric approach to business operations, ultimately leading to increased competitiveness and long-term success.
By understanding these key principles and methodologies, organizations can effectively implement continuous improvement initiatives. These approaches provide the framework and tools necessary to drive change, optimize processes, and foster a culture of continuous learning and growth.
Implementing Continuous Improvement in Business Management
In this section, we will explore the practical steps involved in implementing continuous improvement in business management.
- Setting a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Creating a culture of continuous improvement begins with strong leadership and clear communication. Leaders should emphasize the importance of continuous improvement, encourage employee involvement, and foster a safe environment for sharing ideas and feedback. Regular training and development programs can also help cultivate a mindset of continuous learning and improvement throughout the organization.
- Identifying Areas for Improvement: To effectively implement continuous improvement, it is essential to identify areas that can benefit from enhancement. This involves analyzing existing processes, gathering feedback from employees and customers, and utilizing performance data to pinpoint opportunities for improvement. Engaging employees in this process can provide valuable insights and generate ownership for improvement initiatives.
- Developing Improvement Strategies: Once areas for improvement are identified, it is crucial to develop effective strategies for implementation. This includes setting specific goals, defining key performance indicators (KPIs), and outlining action plans. Collaborative problem-solving techniques, such as brainstorming sessions and cross-functional teams, can aid in generating innovative improvement strategies.
- Implementing Changes: Implementing continuous improvement involves making changes to existing processes, systems, or structures. It is essential to communicate these changes clearly to all stakeholders and provide the necessary support and resources for successful implementation. Regular monitoring and evaluation of the implemented changes will help gauge their effectiveness and make further adjustments if needed.
- Sustaining Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement is an ongoing process. To ensure its sustainability, it is crucial to establish mechanisms for monitoring and reviewing progress regularly. This can involve regular performance reviews, feedback loops, and continuous data collection. Recognizing and celebrating successes along the way can also help maintain momentum and motivation for continuous improvement efforts.
By following these steps and integrating continuous improvement into the fabric of the organization, businesses can foster a culture of innovation, drive operational excellence, and achieve continuous growth and success.
Tools and Techniques for Continuous Improvement
In this section, we will explore various tools and techniques that can support and facilitate continuous improvement efforts in business management.

Process Mapping and Analysis
Process mapping involves visually representing the steps, inputs, and outputs of a process to gain a comprehensive understanding of its flow and identify areas for improvement. Techniques such as value stream mapping and flowcharts help visualize processes and identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and opportunities for streamlining.
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a problem-solving technique used to identify the underlying causes of issues or failures within a process. Tools like the 5 Whys, fishbone diagrams, and fault tree analysis can help uncover the root causes, enabling organizations to implement targeted solutions and prevent recurrence.
Data-driven Decision Making
Data plays a crucial role in continuous improvement. Tools such as statistical process control (SPC), data analytics, and key performance indicators (KPIs) provide insights into process performance, identify trends, and enable data-driven decision making. Collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data helps measure progress, track improvement efforts, and identify areas that require further attention.
Quality Control and Assurance
Quality control techniques, such as checklists, control charts, and Pareto analysis, ensure that products, services, or processes meet defined quality standards. Quality assurance practices, including audits, inspections, and peer reviews, help verify compliance and identify opportunities for improvement in quality management systems.
Benchmarking and Best Practices
Benchmarking involves comparing organizational processes, practices, and performance against industry leaders or best-in-class organizations. By studying and adopting best practices, businesses can gain insights into superior approaches and implement improvements in their own processes. Benchmarking helps identify areas where organizations lag and provides targets for improvement.
These tools and techniques provide valuable support in the continuous improvement journey. By leveraging them effectively, organizations can enhance their problem-solving capabilities, drive process efficiencies, and achieve sustainable improvement in business management practices.
Overcoming Challenges in Continuous Improvement
Implementing continuous improvement in business management can present various challenges. In this section, we will address some common obstacles and provide strategies for overcoming them.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a natural human reaction that can hinder the adoption of continuous improvement initiatives. To overcome this challenge, it is crucial to communicate the purpose and benefits of change, involve employees in the decision-making process, and provide training and support to help them navigate the transition. Creating a culture that embraces change and recognizes the value it brings can also help overcome resistance.
Overcoming Obstacles – Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template
Lack of Resources and Support
Insufficient resources and support can impede continuous improvement efforts. Organizations should allocate dedicated resources, such as time, personnel, and technology, to support improvement initiatives. Providing training and development opportunities for employees and fostering a supportive environment where ideas are encouraged and rewarded can also address resource limitations.
Sustaining Momentum and Avoiding Complacency
Continuous improvement requires ongoing commitment and sustained momentum. One challenge is avoiding complacency when initial improvements have been achieved. To address this, organizations should set challenging goals, celebrate successes, and continuously communicate the importance of maintaining improvement efforts. Regular performance reviews and ongoing feedback loops can help identify areas for further improvement and ensure the continuous learning and growth mindset is upheld.
By acknowledging and proactively addressing these challenges, businesses can mitigate potential roadblocks and create an environment that supports and sustains continuous improvement efforts. Overcoming resistance to change, providing adequate resources and support, and maintaining momentum are key strategies for long-term success in continuous improvement endeavors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, continuous improvement is a vital aspect of business management that drives ongoing growth and success. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can adapt to changing market dynamics, exceed customer expectations, and create a foundation for long-term success. Embracing continuous improvement is a strategic decision that empowers businesses to thrive in a rapidly evolving world.

