This article explores the importance of financial management in business operations and provides insights into various aspects of financial management that contribute to maximizing success.
The article covers topics such as financial planning and budgeting, financial analysis and forecasting, cash flow management, risk management and mitigation, and implementing financial management practices, for achieving business success.
With this text, we continue a series of eight articles dedicated to business management.
This article showcases a range of presentation templates from the PoweredTemplate library that are tailored to the topic of financial management in business operations. They serve as valuable visual aids for business professionals seeking to elevate their presentations and effectively convey the importance of financial management in business operations to their teams and stakeholders.
Table of Contents
- Importance of Financial Management in Business Operations
- Understanding Financial Management
- Financial Planning and Budgeting
- Financial Analysis and Forecasting
- Cash Flow Management
- Risk Management and Mitigation
- Implementing Financial Management Practices
- Conclusion
Importance of Financial Management in Business Operations
In today’s competitive business landscape, the importance of financial management cannot be overstated. It enables organizations to maintain a strong financial position, mitigate risks, and make informed strategic decisions. By effectively managing finances, businesses can allocate resources effectively, control costs, and optimize cash flow. This, in turn, empowers them to seize opportunities, navigate economic challenges, and achieve their operational goals.
Financial management encompasses various aspects, including planning, budgeting, analysis, and forecasting. These functions provide businesses with the necessary insights to make informed decisions and allocate resources appropriately. Financial planning and budgeting help organizations set clear financial goals, establish budgets, and track performance against targets. Financial analysis and forecasting, on the other hand, enable businesses to assess their financial health, identify trends, and anticipate future needs.
Furthermore, financial management involves cash flow management, risk management, and the establishment of effective financial policies and procedures.
Understanding Financial Management
Financial management is a fundamental aspect of business operations, encompassing various key components. Let’s explore the definition, scope, and essential elements of financial management that contribute to the success of organizations.
Definition and Scope of Financial Management
Financial management refers to the strategic planning, organizing, controlling, and directing of financial resources within an organization. It involves managing financial activities to achieve the organization’s goals while ensuring efficient utilization of resources and maximizing shareholder value.
In the context of business operations, financial management encompasses tasks such as financial planning, procurement of funds, investment decisions, risk management, and financial reporting. It involves monitoring financial performance, analyzing financial data, and making informed decisions to optimize the financial health and stability of the organization.
Key Components of Financial Management
Financial management encompasses several key components that are crucial for the success of business operations:
- Financial planning and budgeting;
- Financial analysis and forecasting;
- Cash flow management;
- Risk management and mitigation.
Let’s explore these components in detail.
Financial Planning and Budgeting
Financial planning and budgeting are critical components of effective financial management in business operations. Let’s delve into the significance of financial planning and budgeting and the steps involved in the process.
Importance of Financial Planning and Budgeting
Financial planning and budgeting provide a roadmap for organizations to achieve their financial goals and ensure the efficient allocation of resources. Here are some key reasons why financial planning and budgeting are essential:
- Goal Alignment: Financial planning and budgeting help align financial objectives with the overall business goals. They provide a framework to allocate resources towards strategic initiatives and ensure that financial decisions support the organization’s long-term vision.
- Resource Optimization: By carefully planning and budgeting, organizations can allocate their resources effectively. It allows them to prioritize investments, control costs, and optimize the utilization of financial assets, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and profitability.
- Decision Making: Financial planning and budgeting provide crucial insights for informed decision-making. They enable organizations to evaluate the financial implications of various options, assess risks, and make well-informed choices that align with the organization’s financial capabilities and objectives.
- Performance Monitoring: Financial planning and budgeting serve as benchmarks for monitoring and evaluating financial performance. By comparing actual results against the budgeted targets, organizations can identify deviations, address issues promptly, and take corrective actions to ensure financial stability and success.
Steps Involved in the Financial Planning and Budgeting Process

The financial planning and budgeting process typically involves the following steps:
- Defining Goals: Organizations must clearly define their financial goals, whether it’s revenue growth, cost reduction, profitability improvement, or other specific targets.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering relevant financial data, market trends, and internal information is crucial for accurate financial planning and budgeting. Organizations should analyze historical data and industry insights to inform their financial projections.
- Forecasting: Based on the collected data and analysis, organizations forecast their financial performance for a specific period, typically covering revenues, expenses, and cash flows. This step involves estimating future income, expenses, and capital requirements.
- Budget Development: Using the forecasted financials, organizations create a comprehensive budget that includes revenue targets, expense allocations, and investment plans. The budget should align with the organization’s goals, strategies, and operational needs.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Once the budget is finalized, it is implemented throughout the organization. Regular monitoring of financial performance against the budget is essential to track progress, identify variances, and take corrective actions when necessary.
- Periodic Review and Adjustments: Financial planning and budgeting are iterative processes. Organizations should review their budgets periodically, consider any changes in the business environment, and make adjustments to ensure alignment with the evolving needs and goals of the organization.
By following these steps, organizations can establish a robust financial planning and budgeting process that supports their business operations, facilitates decision-making, and fosters financial stability and growth.
Financial Analysis and Forecasting
Financial analysis and forecasting are vital tools in financial management for business operations. Let’s explore the significance of financial analysis and forecasting, the techniques involved, and how they contribute to effective decision-making.
Significance of Financial Analysis and Forecasting
Financial analysis and forecasting provide valuable insights into an organization’s financial performance, health, and future prospects. Here are some key reasons why financial analysis and forecasting are significant:
- Performance Evaluation: Financial analysis helps assess the organization’s past and current financial performance. It involves examining financial statements, ratios, and key metrics to evaluate profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency. This evaluation aids in identifying areas of strength and weakness and enables corrective measures to be taken.
- Trend Identification: Financial analysis allows the identification of trends and patterns in financial data. By analyzing historical information, organizations can spot emerging trends, changes in customer behavior, market dynamics, and other factors that may impact future financial performance. This insight helps in making proactive decisions to adapt and stay competitive.
- Risk Assessment: Financial analysis helps in evaluating risks associated with financial decisions and operations. It enables organizations to identify potential financial risks, such as liquidity risks, credit risks, market risks, and operational risks. By understanding these risks, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate them and protect their financial stability.
- Future Planning: Financial forecasting enables organizations to estimate future financial outcomes based on historical data, market trends, and anticipated changes. It assists in setting realistic financial goals, making resource allocation decisions, and planning for future investments, expansion, and growth opportunities.
Techniques for Financial Analysis and Forecasting
Several techniques are commonly used for financial analysis and forecasting, including:
- Ratio Analysis: Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting financial ratios that provide insights into an organization’s performance, liquidity, profitability, and efficiency. Examples include liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, and leverage ratios.
- Trend Analysis: Trend analysis examines financial data over time to identify patterns and trends. It helps in understanding the direction and magnitude of changes in financial variables, allowing organizations to make informed decisions based on historical patterns.
- Cash Flow Analysis: Cash flow analysis focuses on assessing the organization’s cash inflows and outflows to understand its ability to generate and manage cash. It helps in determining the organization’s liquidity position and cash flow sufficiency for operations and investment needs.
- Scenario Analysis: Scenario analysis involves developing multiple financial scenarios based on different assumptions and variables. It helps in assessing the potential impact of various factors on financial outcomes and aids in contingency planning and risk management.
Utilizing Financial Analysis and Forecasting for Decision-Making
Financial analysis and forecasting provide valuable information for decision-making in business operations. By leveraging these tools, organizations can:
- Evaluate investment opportunities and assess their financial feasibility.
- Make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and budgeting.
- Identify areas for cost reduction and operational efficiency improvement.
- Assess the financial impact of strategic initiatives and business decisions.
- Evaluate the financial viability of new products, projects, or ventures.
- Monitor financial performance and take corrective actions when deviations occur.

By utilizing financial analysis and forecasting effectively, organizations can enhance their decision-making processes, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall financial management practices for sustainable business success.
Cash Flow Management
Cash flow management plays a crucial role in the financial management of business operations. Let’s delve into understanding cash flow and its importance, as well as explore strategies for effective cash flow management.
Understanding Cash Flow and Its Importance
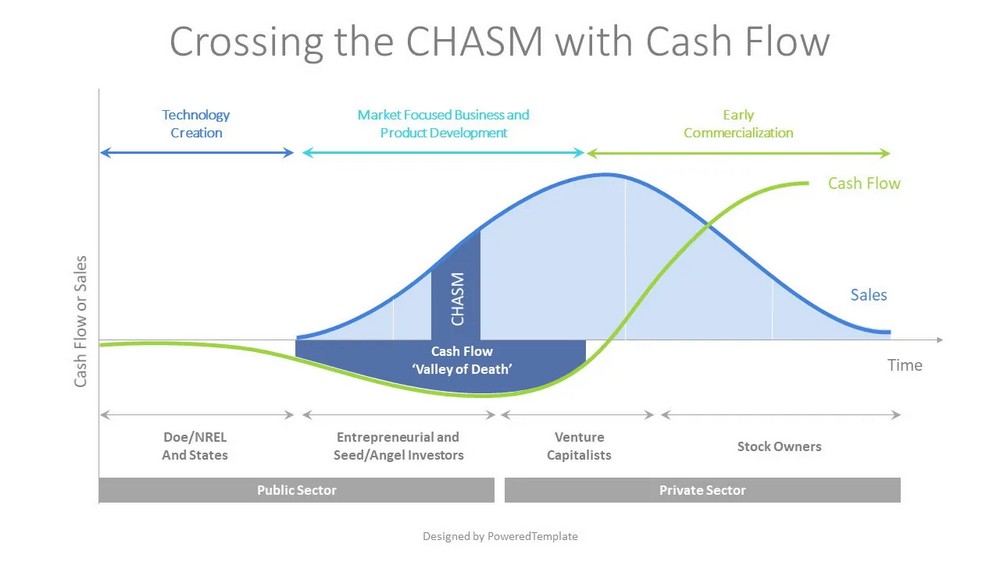
Cash flow refers to the movement of money into and out of a business. It represents the inflow and outflow of cash from various sources such as sales, investments, loans, and expenses. Understanding cash flow is essential for the following reasons:
- Liquidity: Cash flow provides insight into the organization’s liquidity position. It determines the ability to meet short-term financial obligations, such as paying suppliers, employees, and utility bills. Sufficient cash flow ensures the smooth functioning of daily operations.
- Financial Stability: Maintaining positive cash flow is crucial for the financial stability of an organization. It allows for the timely payment of debts, interest, and other financial obligations. A healthy cash flow position reduces the risk of insolvency and financial distress.
- Business Growth: Positive cash flow enables organizations to fund growth initiatives, invest in research and development, expand operations, or seize new business opportunities. It provides the necessary financial resources to fuel sustainable growth and innovation.
Strategies for Effective Cash Flow Management

Implementing effective cash flow management practices is vital to ensure the stability and growth of business operations. Here are some strategies to optimize cash flow:
- Monitor and Forecast Cash Flow: Regularly monitor and project cash flow by analyzing historical data, sales forecasts, and expected expenses. This enables organizations to anticipate cash gaps or surpluses and take proactive measures.
- Streamline Receivables: Implement efficient processes for collecting payments from customers. Offer incentives for early payments, send timely and accurate invoices, and follow up on outstanding payments promptly. Consider using online payment systems to expedite the collection process.
- Manage Payables: Negotiate favorable payment terms with suppliers to optimize cash flow. Take advantage of early payment discounts when feasible. However, ensure timely payments to maintain good relationships with suppliers.
- Control Expenses: Analyze expenses to identify areas where cost savings can be achieved. Review vendor contracts regularly, seek competitive bids, and consider alternative suppliers or cost-effective alternatives. Manage inventory levels to avoid tying up excessive cash in stock.
- Cash Flow Forecasting: Develop cash flow forecasts to anticipate future cash needs and identify potential shortfalls. This enables proactive measures, such as securing additional financing or adjusting expenditures, to ensure sufficient liquidity.
- Working Capital Management: Optimize working capital by efficiently managing inventory, accounts receivable, and accounts payable. Minimize the time between cash outflows and inflows to maximize available cash.
- Cash Reserves and Financing: Maintain adequate cash reserves to cover unexpected expenses or economic downturns. Explore financing options, such as lines of credit or business loans, to bridge cash flow gaps during lean periods.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can enhance their cash flow management practices, improve liquidity, and maintain financial stability. Effective cash flow management ensures the availability of funds to meet obligations, support growth initiatives, and navigate through financial challenges with confidence.
Risk Management and Mitigation
Risk management and mitigation are integral aspects of financial management in business operations. In this section, we will explore the process of identifying business risks, evaluating risk exposure, and implementing strategies for effective risk mitigation.

Identifying Business Risks
Identifying business risks is a critical first step in risk management. It involves assessing potential threats that could adversely impact the organization’s financial performance, operations, or reputation. Some common business risks include:
- Financial Risks: These include risks related to market volatility, currency exchange rates, interest rates, creditworthiness, liquidity, and financial fraud.
- Operational Risks: Operational risks arise from internal processes, systems, and human factors. They include risks associated with technology, supply chain disruptions, employee errors, regulatory compliance, and business continuity.
- Strategic Risks: Strategic risks pertain to the organization’s ability to adapt to changing market conditions, competition, innovation, and strategic decision-making. These risks can impact the long-term viability and success of the business.
- Reputational Risks: Reputational risks involve potential damage to the organization’s brand image, customer trust, and stakeholder confidence. Negative publicity, customer dissatisfaction, product recalls, or ethical issues can lead to reputational damage.

Evaluating Risk Exposure
After identifying potential risks, organizations need to evaluate their risk exposure. This assessment helps determine the likelihood and potential impact of each risk on the organization. Key steps in evaluating risk exposure include:
- Risk Assessment: Assess the probability of each identified risk occurring and evaluate its potential impact on the organization’s financial performance, operations, and strategic objectives. This analysis helps prioritize risks based on their significance.
- Quantitative Analysis: Utilize quantitative methods to assign numerical values to risks, such as estimating potential financial losses, calculating risk ratios, or using statistical models. This analysis provides a more objective view of risk exposure.
- Qualitative Analysis: Conduct qualitative analysis by considering subjective factors, expert opinions, and judgment to evaluate risks that are difficult to quantify. This analysis complements quantitative assessment and helps capture important risk dimensions.
- Risk Mapping: Visualize risks on a risk map or matrix based on their likelihood and impact. This mapping helps in identifying high-risk areas that require immediate attention and developing appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
Strategies for Risk Mitigation
Once risks are identified and their exposure is evaluated, organizations can implement strategies to mitigate and manage these risks effectively. Some strategies for risk mitigation include:
- Risk Avoidance: Avoid or minimize high-risk activities or investments that could expose the organization to significant financial, operational, or reputational risks.
- Risk Transfer: Transfer or share risks with external parties through insurance, contracts, or partnerships. This strategy helps reduce the financial impact of risks by transferring them to specialized entities.
- Risk Reduction: Implement measures to reduce the likelihood or impact of risks. This can involve improving internal controls, implementing security measures, diversifying business operations, or enhancing employee training and awareness.
- Risk Retention: Accept certain risks that are manageable or essential for business growth. However, establish contingency plans and allocate resources to mitigate the impact of these risks if they materialize.
- Business Continuity Planning: Develop robust business continuity plans to ensure the organization can effectively respond to and recover from potential disruptions or disasters. This includes identifying critical processes, establishing backup systems, and conducting regular drills and testing.
By implementing comprehensive risk management practices and strategies, organizations can proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks that may impact their financial stability, operational efficiency, and reputation. Effective risk management enhances resilience, fosters trust among stakeholders, and safeguards the long-term success of the business.
Implementing Financial Management Practices
Implementing effective financial management practices is crucial for maximizing success in business operations. This section will explore key aspects of implementing financial management, including establishing financial management policies and procedures, utilizing financial management tools and software, training and developing the finance team, and monitoring and evaluating financial performance.
Establishing Financial Management Policies and Procedures
Establishing robust financial management policies and procedures provides a framework for maintaining financial discipline and transparency within an organization. Some key considerations for establishing financial management policies and procedures include:
- Budgeting and Expense Control: Develop a comprehensive budgeting process that aligns with strategic objectives and enables effective expense control. Establish guidelines for expenditure approval, reimbursement procedures, and financial reporting requirements.
- Financial Reporting and Record-Keeping: Define standards for financial reporting and record-keeping, including the frequency, format, and content of financial statements. Ensure compliance with relevant accounting standards and regulations to maintain accurate and reliable financial records.
- Internal Controls: Implement internal control systems to safeguard assets, prevent fraud, and ensure compliance with financial policies and regulations. This includes segregation of duties, regular internal audits, and establishing approval processes for financial transactions.
- Risk Management Framework: Integrate risk management principles into financial management policies and procedures. This involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks to protect the organization’s financial assets and optimize risk-reward trade-offs.
Utilizing Financial Management Tools and Software

Financial management tools and software play a critical role in streamlining financial processes, enhancing accuracy, and providing valuable insights. Organizations should leverage appropriate tools and software to:
- Financial Planning and Budgeting: Utilize dedicated software for financial planning and budgeting, enabling efficient budget creation, scenario modeling, and variance analysis. These tools help optimize resource allocation and improve forecasting accuracy.
- Financial Analysis and Reporting: Implement software for financial analysis and reporting, allowing for detailed financial performance analysis, ratio calculations, and graphical presentations. These tools provide deeper insights into financial data and facilitate informed decision-making.
- Cash Flow Management: Utilize cash flow management software to monitor cash inflows and outflows, forecast cash flow projections, and manage liquidity effectively. Such tools enable organizations to track and optimize cash flow in real-time.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Implement risk assessment and management software to identify, assess, and mitigate financial risks. These tools facilitate risk mapping, risk quantification, and scenario analysis, supporting proactive risk management practices.
Training and Developing the Finance Team
Investing in the training and development of the finance team is crucial for ensuring their proficiency in financial management practices. Organizations should:
- Technical Skills Enhancement: Provide training programs to enhance the team’s technical skills in areas such as financial analysis, budgeting, forecasting, and risk management. This equips them with the necessary knowledge and tools to perform their roles effectively.
- Professional Certifications: Encourage and support finance team members in obtaining relevant professional certifications, such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA). These certifications validate their expertise and enhance their credibility.
- Continual Learning: Foster a culture of continual learning and professional development within the finance team. Encourage participation in seminars, workshops, webinars, and industry conferences to stay updated with the latest trends and best practices in financial management.
Monitoring and Evaluating Financial Performance
Regular monitoring and evaluation of financial performance are essential to ensure the effectiveness of financial management practices. Organizations should:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define and track KPIs that reflect the organization’s financial health, efficiency, and profitability. These may include metrics like revenue growth, profit margins, return on investment (ROI), and cash conversion cycle.
- Financial Reporting and Analysis: Conduct regular financial reporting and analysis to assess the organization’s performance against targets and identify areas for improvement. Utilize financial ratios, trend analysis, and benchmarking to gain insights into financial performance.
- Periodic Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of financial management policies, procedures, and systems to ensure their relevance and effectiveness. Identify any gaps or areas that require refinement and make necessary adjustments.
- Board and Stakeholder Reporting: Provide regular financial reports to the board of directors and stakeholders, communicating financial performance, risks, and strategic financial goals. Transparency in financial reporting builds trust and facilitates informed decision-making.
By implementing robust financial management practices, utilizing appropriate tools and software, investing in the development of the finance team, and monitoring financial performance, organizations can optimize their financial operations, mitigate risks, and drive sustainable growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial management serves as a strategic tool for maximizing success in business operations. By understanding its key components, implementing best practices, and leveraging modern tools and techniques, businesses can navigate complexities, mitigate risks, and achieve sustainable growth in today’s dynamic economic landscape.